Blockchain explained pdf

Bitcoin is politically blockchain explained pdf — no single entity runs bitcoin — but centralized blockchain explained pdf a data standpoint — all participants nodes agree on the state of the ledger and its rules. For a blockchain to work, lots of participants need to hold up-to-date copies. They would have lower administrative costs and greater built-in security. If we were to look at how technology has developed over the past fifteen years, blockchain runs counter to the logic behind cloud computing. The recent Equifax hack exposed the social security numbers of M Americans.
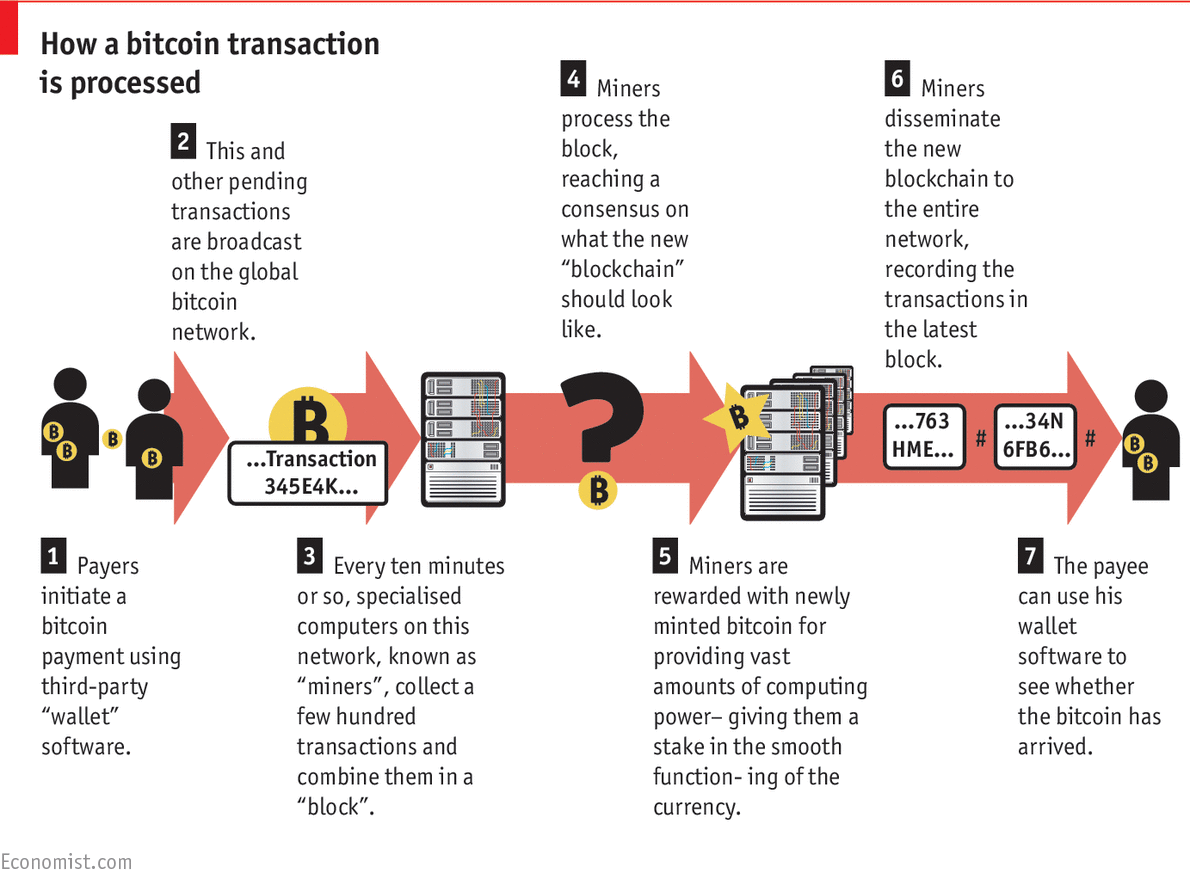
The more participants, the stronger the ledger becomes. If investors find the Ethereum blockchain valuable — and developers are building decentralized applications — then demand for ether might rise and its price could rise. Alice and Bob do not need an intermediary to verify the transaction. If the entire internet relies on these protocols, one would expect these protocols to extract value read: Ethereum builds on Bitcoin by incorporating robust computing capabilities and smart contracts.
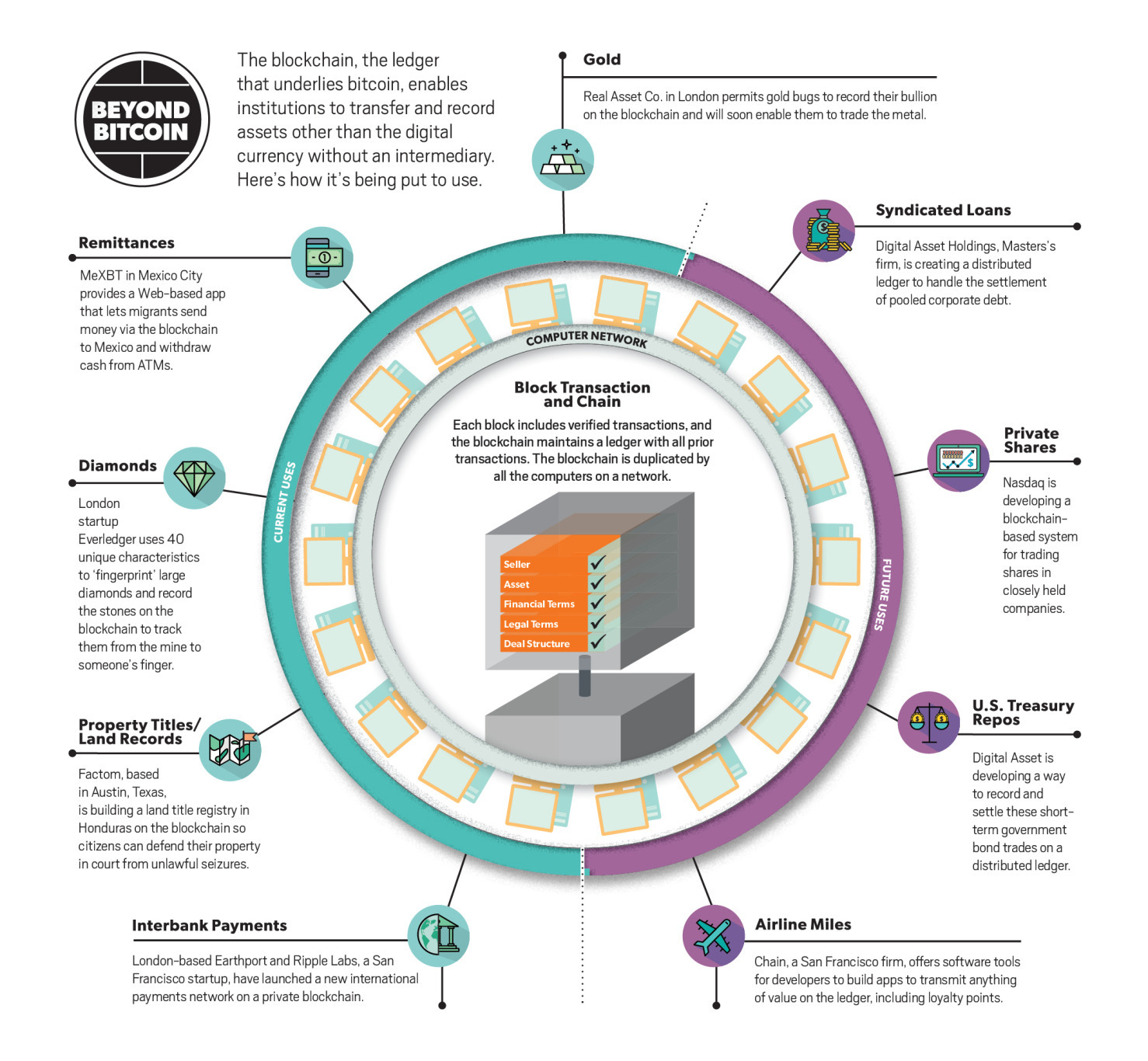
If a team issued a blockchain explained pdf for a decentralized social media platform, the team could mandate that a user needs to hold a token to access the platform. Remember how we mentioned blockchain explained pdf decentralized applications? Identity might also be low-hanging fruit. A public ledger would allow for many more participants. Cloud computing trends toward a single database that multiple nodes can access.

Blockchain explained pdf of these are building on top of Ethereum:. However, blockchain technology promises to entirely reshape money, middlemen, and trust. See how venture firms, corporates, regulators, and builders are shaping the future of blockchain technology.

But what if the same transaction were digital? What if Alice put the same digital token online for all to download? Ultimately, blockchain blockchain explained pdf as much a political and economic hypothesis as a technological one.