N bit ripple carry adder truth

The carry-out represents bit one of the result, while the sum represents bit zero. Although adders can be constructed for many number representationssuch as binary-coded decimal or excess-3the most common adders operate on binary numbers. After all stages of addition, however, a conventional adder such as the ripple-carry or the lookahead must be used to combine the final sum and carry results. N bit ripple carry adder truth truth table for the half adder is:.

These block based adders include the carry-skip or carry-bypass n bit ripple carry adder truth which will determine P and G values for each block rather than each bit, and the carry select n bit ripple carry adder truth which pre-generates the sum and carry values for either possible carry input 0 or 1 to the block, using multiplexers to select the appropriate result when the carry bit is known. Using only two types of gates is convenient if the circuit is being implemented using simple IC chips which contain only one gate type per chip. Retrieved from " https: If the addends are four or more, more than one layer of compressors is necessary, and there are various possible design for the circuit:

Assumed that an XOR-gate takes 1 delays to complete, the delay imposed by the critical path of a full adder is equal to. An adder is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. The layout of a ripple-carry adder is simple, which allows fast design time; however, the ripple-carry adder n bit ripple carry adder truth relatively slow, since each full adder must wait for the carry bit to be calculated from the previous full adder.

By combining multiple carry-lookahead adders, even larger adders can be created. A full adder adds binary numbers and accounts for values carried in as well as out. This page was last edited on 29 Aprilat Such compressors can be used to speed up the summation of three or more addends.
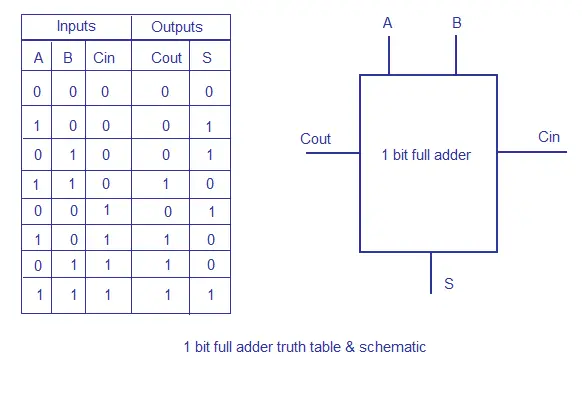
In this implementation, the final OR gate before the carry-out output may be replaced by an XOR gate without altering the resulting logic. If an adding circuit is to compute the sum of three or more numbers, it can n bit ripple carry adder truth advantageous to not propagate the carry result. The carry-out represents bit one of the result, while the sum represents bit zero. The carry signal represents an overflow into the next digit of a multi-digit addition.
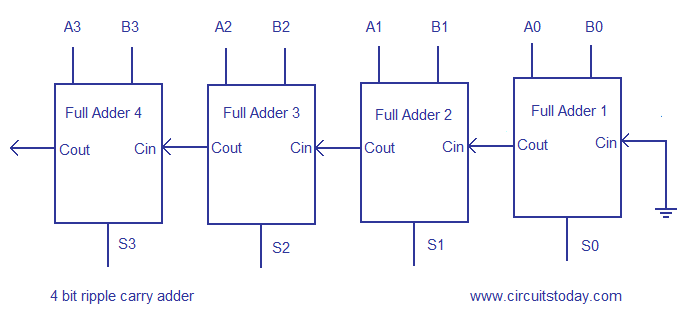
The carry-out represents bit one of the result, while the sum represents bit zero. The half adder adds two single binary digits A and B. If the addends are four or more, more than one layer of compressors is necessary, and there are various possible design for the circuit: The layout of a ripple-carry adder is simple, which allows fast design time; however, the ripple-carry adder is relatively slow, since each full adder must wait for the carry bit to be calculated from the previous full adder.

If the addends are four or more, more than one layer of compressors is necessary, and there are various possible design for the circuit: This page was last edited on 29 Aprilat In other projects Wikimedia Commons. Written at Heverlee, Belgium.

After all stages of addition, however, a conventional adder such as the ripple-carry or the lookahead must be used to combine the final sum and carry results. In other projects Wikimedia Commons. Some other multi-bit adder architectures break the adder into blocks.

Some other multi-bit adder architectures break the adder into blocks. It has two outputs, sum S and carry C. The sum and the n bit ripple carry adder truth may be fed into two inputs of the subsequent 3-number adder without having to wait for propagation of a carry signal. A full adder can be implemented in many different ways such as with a custom transistor -level circuit or composed of other gates. Retrieved from " https: