Tapscott blockchain stock
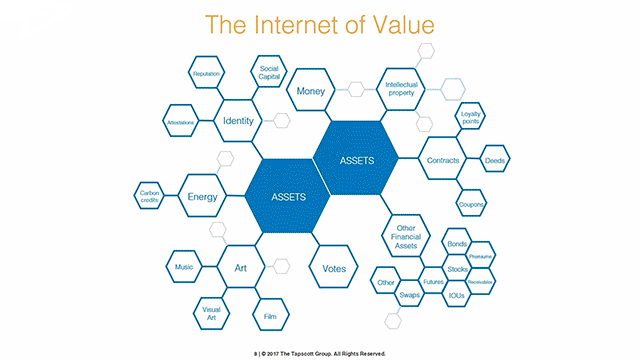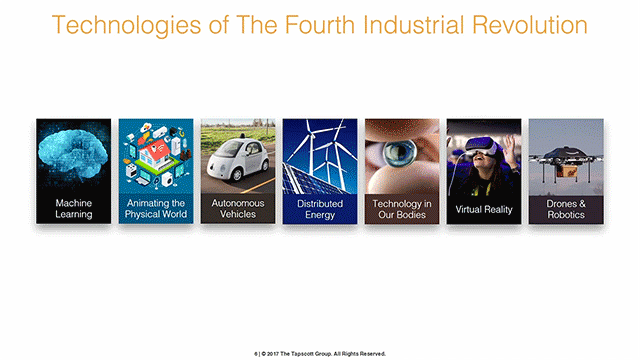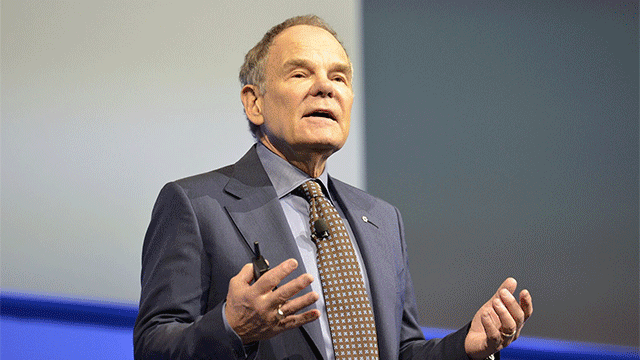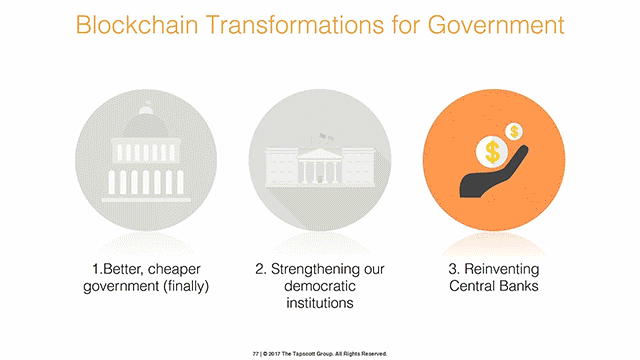
Understanding how blockchain works is very complicated, but at its root is a new digital medium for value. Simply put, it is a vast, global, distributed ledger where buyers and sellers can securely and privately transfer, store, and manage anything of value without using a bank or credit card.
High levels of encryption protect the transaction by validating the parties involved and by preventing hacking, erasure or amendments. The SEC provided a very nuanced perspective — saying rightly that certain digital assets are securities and that a facts-based approach should be applied every time to make that determination.
Put another way, enterprises and individuals can directly raise money from investors through crowdfunding by selling ownership using cryptocurrency instead of going through the red tape and the high cost of issuing shares or debt.
Countries, and their central banks, can do the same and blockchain technology is being studied by those who now print currencies such as the Bank of England, the Bank of Canada, the Federal Reserve in the U. For instance, a retail consumer can buy goods digitally without large credit card fees and the shopkeeper will have the proceeds deposited immediately into his bank account.
This would mean lower prices for consumers and higher profit margins for the shopkeeper. To boot, encryption prevents counterfeiting, fraud, or tampering. In mining, a blockchain digital record can permanently register core samples or contracts; and in trade, a blockchain record can enshrine bills of lading, letters of credit and contractual terms globally.
Uber and AirBnB or stock exchanges can be replaced with platforms that directly link buyers and sellers without the use of large corporations in between. Adoption accelerates as stronger protocols are devised. Anyone can copy and change it. As a result, we use intermediaries to establish trust and maintain integrity. Banks, governments, and in some cases big technology companies have the ability to confirm identities so that we can transfer assets; the intermediaries settle transactions and keep records.
For the most part, intermediaries do an adequate job, with some notable exceptions. One concern is that they use servers that are vulnerable to crashes, fraud, and hacks.
Another is that they often charge fees — for example, to wire money overseas. And sometimes, they make terrible mistakes, as the financial crisis made evident. What would happen if there were an internet of value where parties to a transaction could store and exchange value without the need for traditional intermediaries? Sign in , buy as a PDF or create an account. How Blockchain Will Change Organizations Igor Ageyev December 13, A firm or organisation as an subject of economy or society and a management function are complex systems which require deep analysis of potential changes and possible impacts and risks.
It is good that authors believe in many points they state but without analysis of environment and relation with other components at least at theoretical level it sounds more like a fantasy. Firstly, thank you for the article, and the such a great description of what Blockchain and Bitcoin technologies are capable of changing. But, I have a few questions? So, if all negotiations are based on the actual existing facts and figures based on transactions only, in many cases can diminish the value of strategic intents of organizations that have possible future innovations and other roadmap enhancement to offer, but are unable to present the facts to the database for IP or other reasons.
How do we account for these very important vales? Blockchain could change federal reserve bank or central bank the way they are processing transactions. Alternatively, Blockchain would bring trusted processing of transactions closer to consumers without inter-mediate brokers, this means the existing purpose of the banks and central banks gets eliminated over time.