Blockchain distributed ledger explained

In today's connected and integrated world, economic activity takes place in business networks that span national, geographic, and jurisdictional boundaries. Other possible uses beside cryptocurrencies include Smart Contracts First introduced by Ethereum or file storage. These risks and uncertainties contribute to missed business opportunities.

They wanted to see what would happen and generate interest on campus. They are inefficient, costly, and subject to misuse and tampering. Figure it out now.

The bitcoin-based consumer payment industry cooled down. Transactions typically involve various participants like buyers, sellers, and intermediaries such as banks, auditors, or notaries whose business agreements and contracts are recorded in ledgers. Catalini, together with Professor Catherine Tucker, blockchain distributed ledger explained the experiment and studied the results.

The network can also exist between individualswho might need to store data, digital assets, or contracts on the blockchain, for example. Every record in the distributed ledger has a timestamp and unique cryptographic signature, thus making the ledger an auditable, immutable history of blockchain distributed ledger explained transactions in the network. Retrieved 21 November

At its core, the system records blockchain distributed ledger explained chronological order of blockchain distributed ledger explained with all nodes agreeing to the validity of transactions using the chosen consensus model. Web browser company Brave uses a blockchain to verify when users have viewed ads and, in turn, pays publishers when those same users consume content. Within an organization, a blockchain network could be used to share reference data between divisions or to create an audit or compliance network, for example. They may also be mineable you can claim ownership of new coins contributing with a node or not mineable the creator of the cryptocurrency owns all at the beginning.

Sign up there to receive updates with the latest and most important MIT work about blockchain. They are inefficient, costly, and subject to misuse and tampering. Blockchain was first introduced to the market as the technology underpinning Bitcoin exchangesbut its practical uses in the world of business extend far beyond blockchain distributed ledger explained transactions.
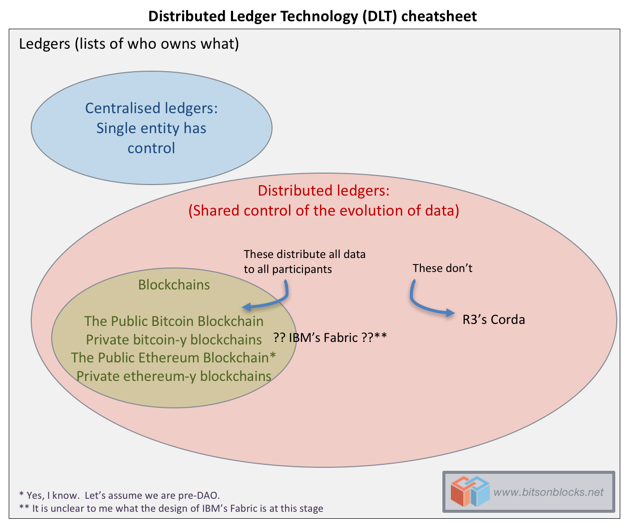
Sending secure messages that carry value does not require a bank or PayPal in the middle anymore. Because no one participating member blockchain distributed ledger explained the source of origin for information contained in the shared ledger, blockchain technologies lead to increased trust and integrity in the flow of transaction information among the participating members. Ready to go deeper?