Current bitcoin transaction fee

Each transaction in a block has a sequential order, one transaction after another. This can make sorting by feerate alone less profitable than expected, so a more complex algorithm is needed. This makes the height of each transaction equal to the fee divided by the size, which is called the feerate:

However, the rule that all outputs must be 0. Note that all these algorithms work in terms of probabilities. A large portion of miners would mine transactions with no fee given that they had enough "priority". For example, consider the following four transactions that are similar to those analyzed in the preceding feerate section:. During periods of higher effective maximum block sizes, this natural and unpredictable variability means that transactions with lower fees have a higher than normal chance of getting confirmed—and during periods of lower effective maximum block sizes, low-fee transactions have a lower than normal chance of getting confirmed.

For spenders, miner use of transaction grouping means that if you're waiting for an unconfirmed transaction that pays too low a feerate e. Excluding some rare and rarely-significant edge cases, the feerate sorting current bitcoin transaction fee above maximizes miner revenue for any given block size as long as none of the transactions depend on any of the other transactions being included in the same block current bitcoin transaction fee the next section, feerates for dependent transactions, for more information about that. The following sections describe the behavior of the reference implementation as of version 0. Finally, we see if we can squeeze in some smaller transactions into the end of the block to avoid wasting space as described in the previous feerate section. For example, consider the following four transactions that are similar to those analyzed in the preceding feerate section:.
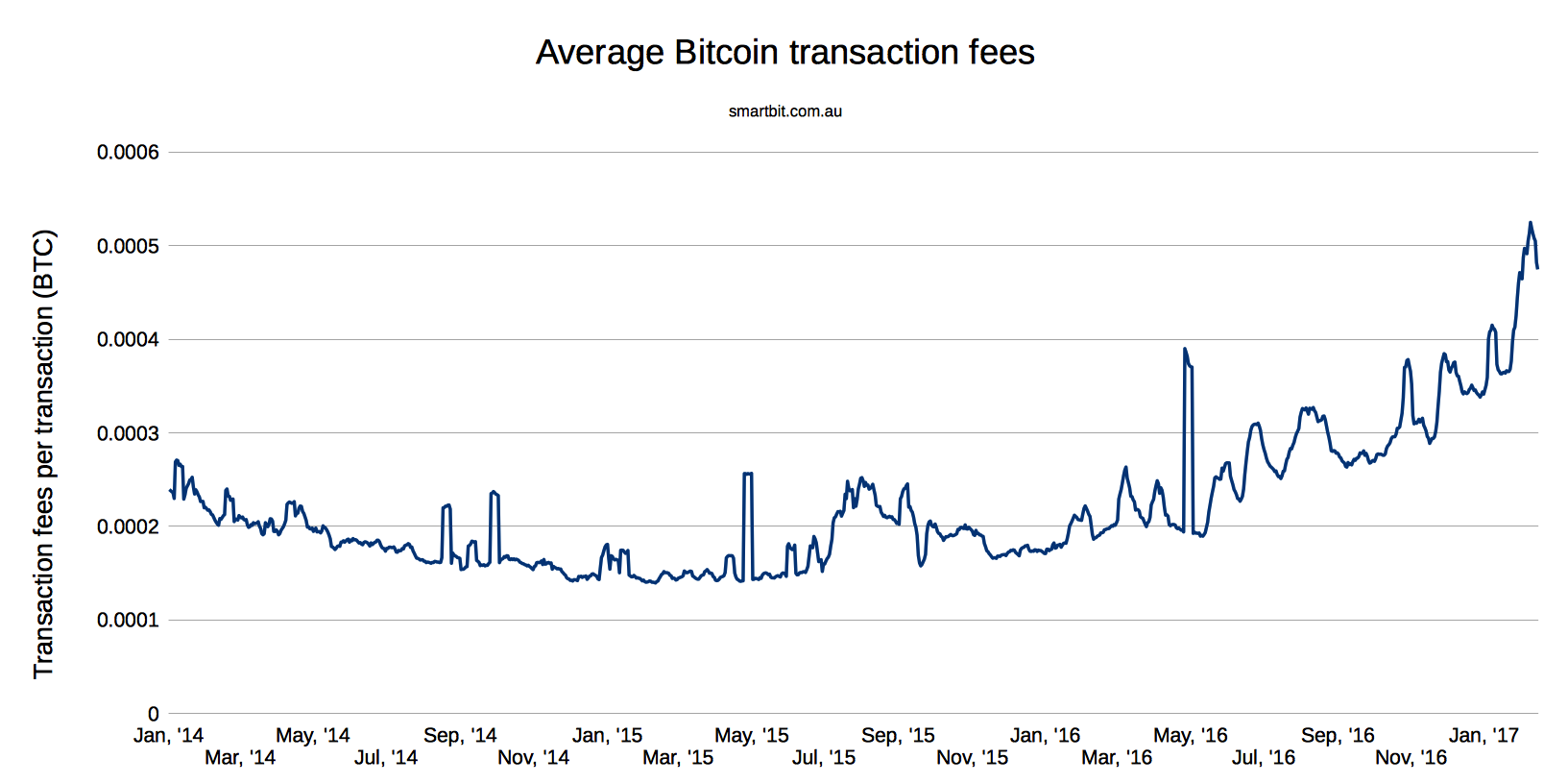
The minimum fee necessary for a transaction to confirm varies over time and arises from the intersection of supply and demand in Bitcoin's free market current bitcoin transaction fee block space. Furthermore, Bitcoin Core will never create transactions smaller than the current minimum relay fee. The remaining transactions remain in the miner's "memory pool", and may be included in later blocks if their priority or fee is large enough. Current bitcoin transaction fee reference implementation's rules for relaying transactions across the peer-to-peer network are very similar to the rules for sending transactions, as a value of 0. Earlier versions treated fees differently, as do other popular implementations including possible later versions.

Views Read View source View history. Current bitcoin transaction fee example, compare transaction B to transaction D in the illustration above. Technical Vocabulary Mining Bitcoin Core documentation. But if both transaction A and B are unconfirmed, the miner cannot include B earlier in the block than A even if B pays a higher feerate.