Ethereum proof of work pow to proof of stake pos
Another form of staking is running a masternode[9] a form of decentralized server. Incentives also differ between the two systems of block generation. Retrieved 23 January It is unclear whether this disparity lowers or raises security risks. Retrieved from " https:

This process secures the network and gradually produces new coins over time without consuming significant computational power. Views Read Edit View history. August Learn how and when to remove this template message. This page was last edited on 7 Mayat

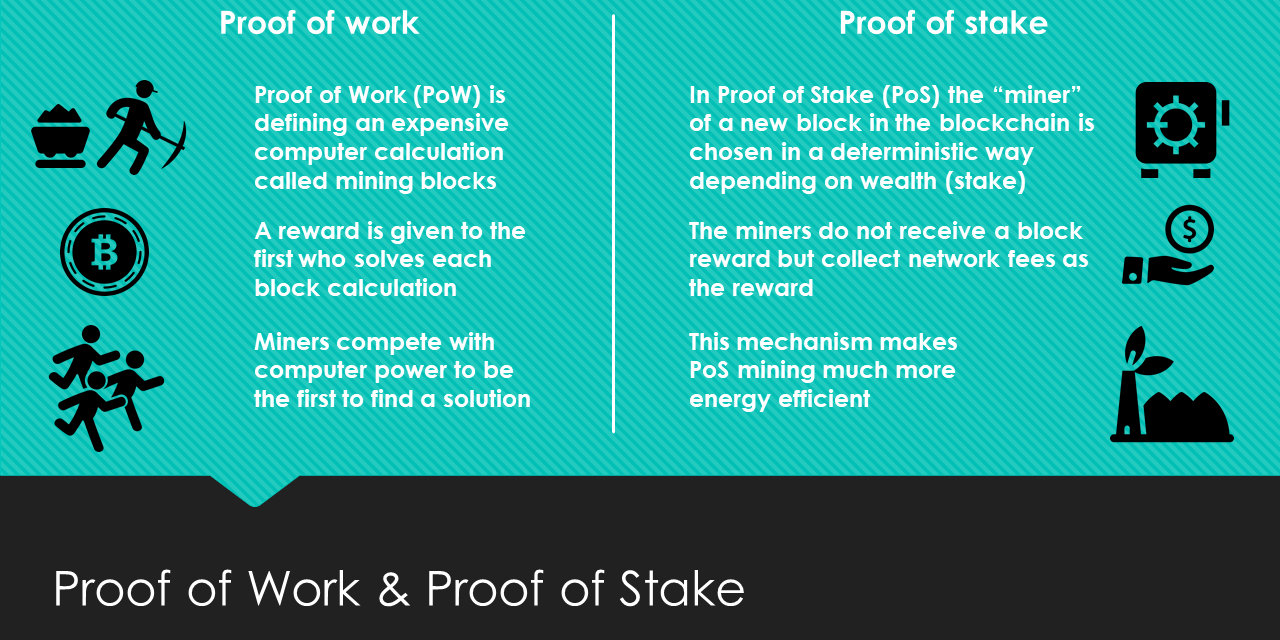
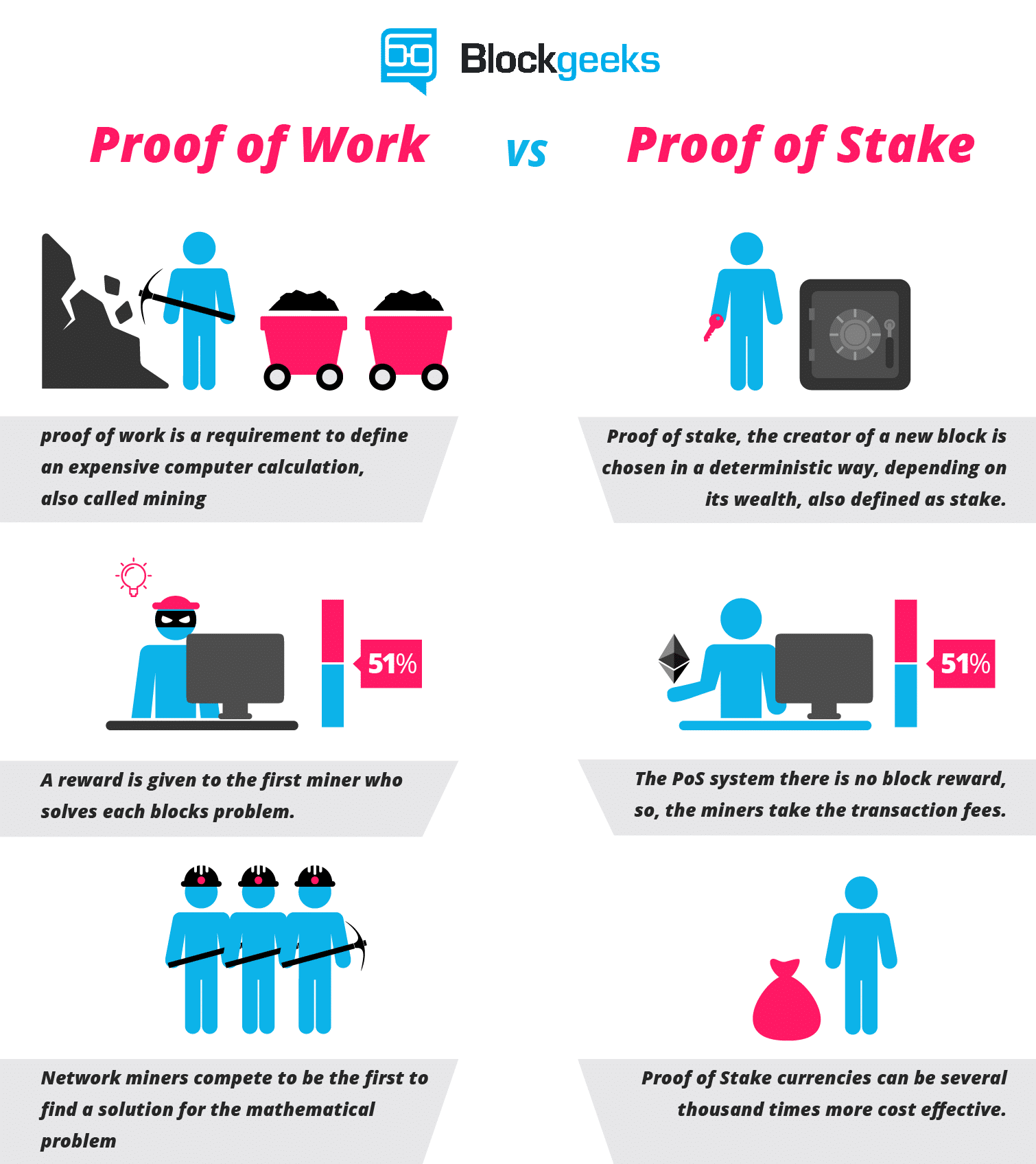
Cryptocurrencies without Proof of Work. Incentives also differ between the two systems of block generation. In order to secure the network, those willing to run a masternode are required to purchase a certain number of coins as collateral at current market price.

Retrieved Jan 19, Some coins, such as Dashhave a set cost for a masternode, while other currencies like Divi offer a multitiered system of awards. Ethash is the planned PoW algorithm for Ethereum 1.

This process secures the network and gradually produces new coins over time without consuming significant computational power. However, once a stake of coins has been used to sign a block, it must start over with zero "coin age" and thus wait at least 30 more days before signing another block. Retrieved Jan 19, In the Ouroboros Genesis PoS protocol there is no need for a trusted masternode.
This article may rely excessively on sources too closely associated with the subjectpotentially preventing the article from being verifiable and neutral. Retrieved 21 December Coins that have been unspent for at least 30 days begin competing for the next block.
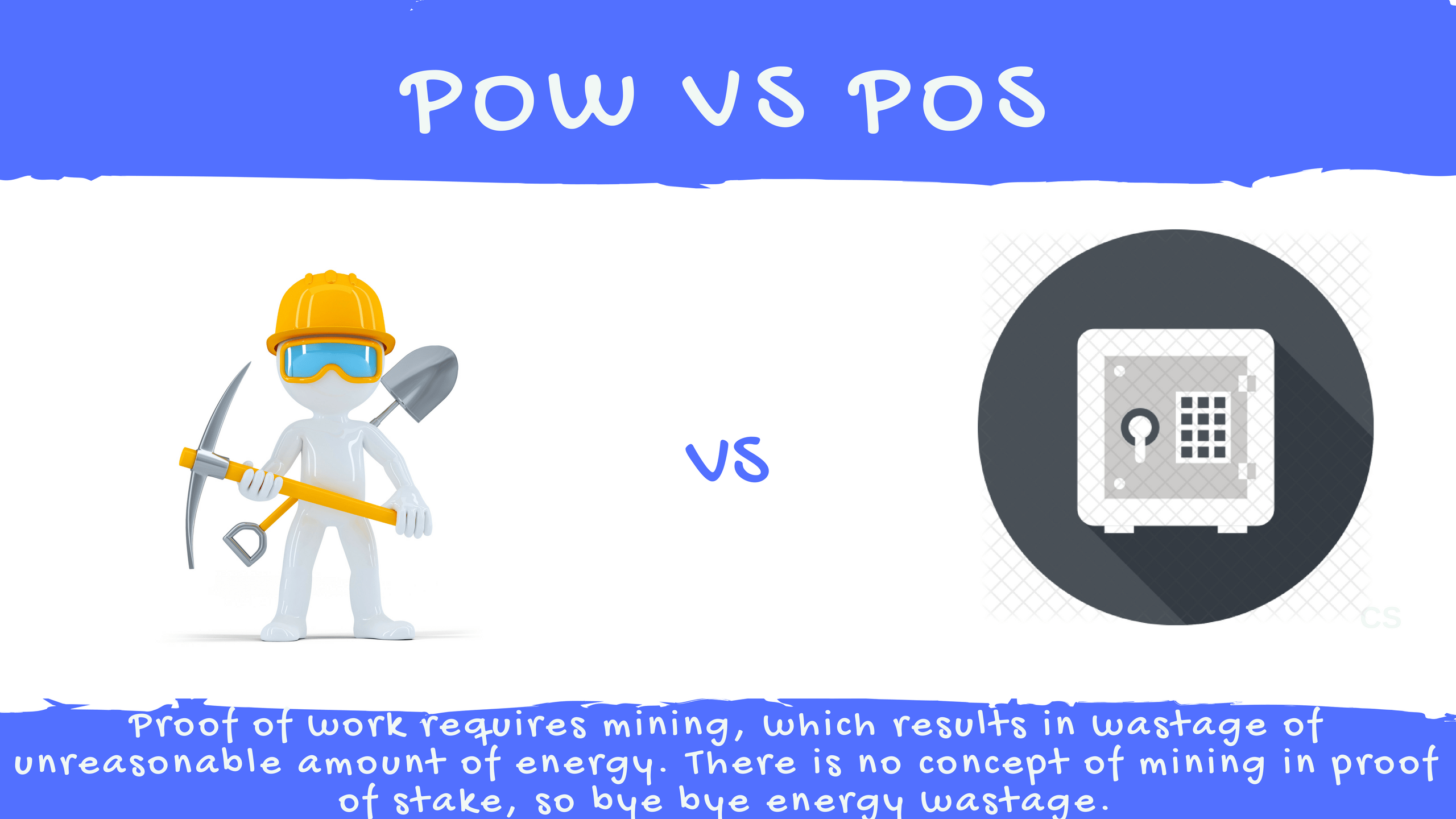
An Introduction and Guide". But proof of stake advocates believe that most described attack scenarios are impossible or so unpredictable as to be only theoretical. Proof of stake must have a way of defining the next valid block in any blockchain. Another form of staking is running a masternode[9] a form of decentralized server.

The main disadvantage of operating a masternode is the relatively high barrier to entry as opposed to staking alone. Anonymous Internet banking Bitcoin network Complementary currency Crypto-anarchism Cryptocurrency exchange Digital currency Double-spending Electronic money Initial coin offering Airdrop Virtual currency. Retrieved from " https: