How bitcoin confirmations work
A confirmation is when a transaction makes its way from the transaction pool in to the blockchain. When you make a bitcoin transaction, you're basically inserting a line of data in to the bitcoin network. This transaction data then gets relayed from node to node, until everyone on the network holds a copy of your transaction.
But initially, new bitcoin transactions are held the "memory pools" of each node. This is like temporary memory on the bitcoin network. So until a transaction is "confirmed" and gets written in to the blockchain, it hasn't been permanently stored on the bitcoin network. There are so many transactions taking place all over the network and at the same time that it makes it difficult for the entire network to agree on the order of each one. This is why new transactions get stored in memory pools at first, before being written how bitcoin confirmations work the blockchain.
The only way you can "reverse" a transaction in bitcoin is by trying to use the bitcoins you're sending in one transaction in a second transaction. I owe you 1 bitcoin. So I create a transaction that sends this bitcoin to how bitcoin confirmations work address, and I insert it in to the network.
However, I decide I don't want to send you this bitcoin anymore. So before this transaction propagates the entire bitcoin network, I also create a second transaction that sends this bitcoin to a different address one that I ownand I insert it in to a different node on the network. You can't delete how bitcoin confirmations work transaction from the memory pool; the only thing you can do is try and "overwrite" it.
As a result, there are now two competing transactions on the bitcoin network that are trying to send the same bitcoin to different addresses. For this to have a chance of working, I have how bitcoin confirmations work insert the second transaction in to the bitcoin almost instantly after the first. Nodes will reject "duplicate" transactions, so if the first transaction gets relayed to every node on the network by the time I try and insert the second, it's not going to get very far. Even if you try and reverse a transaction in the memory pool by sending a second one in at the same timethere's no how bitcoin confirmations work that you're going to be able to shaft the original recipient… the first transaction could just as easily be the one that makes it in to the blockchain.
How bitcoin confirmations work you run the bitcoin software and turn mining "on", your node will do this:. SHA spits out much bigger numbers than this, but don't worry about that — this is just an example. Bitcoin deals with huge numbers, so finding a number that works takes a lot of processing power and luck. Therefore, although anyone can find a number that works at any time, all the competition makes how bitcoin confirmations work very difficult for a single person to do it.
This is why mining exists — to make it so that no one is able to single-handedly control the transactions that get added to the blockchain. Here's a another explanation of how bitcoin mining works. So effectively, if someone is waiting for a "confirmation" they are how bitcoin confirmations work for the news that the transaction has become permanent, and that the bitcoins they have just been sent are not going to end up somewhere else.
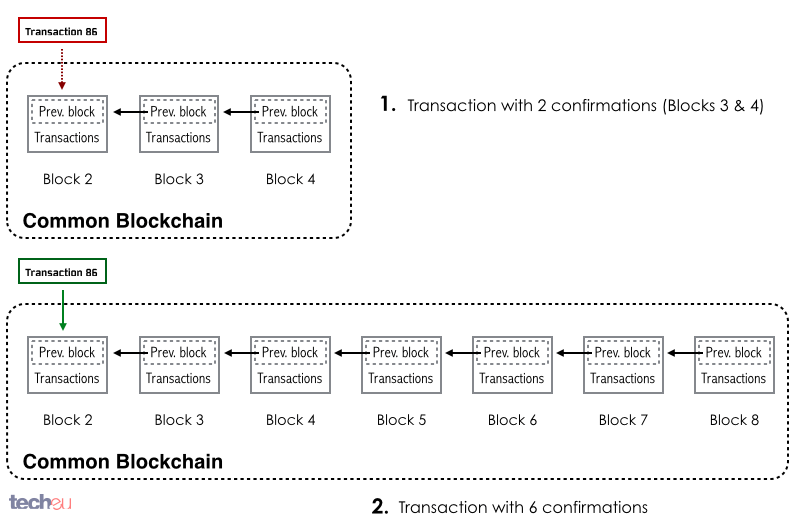
How bitcoin confirmations work first confirmation is when a transaction makes it in to the blockchain for the first time. All additional confirmations are simply when new blocks get mined on top of it.
So when you see that a transaction has " X confirmations ", it makes more sense to think of it as being X blocks deep in the blockchain. Because even if a transaction gets in to the blockchain, it's actually possible for it to make its way back in to the memory pool. I know, I somewhat lied about transactions not being able to make it out of the blockchain.
Ocassionally two or more miners will mine a block at same time. If this happens, both of these blocks will get relayed around the network. Nodes will try and build upon whichever block they receive first, which means that half the network will be how bitcoin confirmations work to build on one block of transactions, and the other half on the other.
So if you look at the overall picture of the blockchain, it will look like a "fork". But forks aren't a problem, because eventually another new block wil be mined, extending one of the chains it doesn't matter which. One chain will now be longer than the competing one, so when nodes receive this latest block, they will adopt the longest chain and ditch the shorter one because nodes always look to how bitcoin confirmations work on the longest chain available.
So as how bitcoin confirmations work can see, forks are natural and harmless. However, some people like how bitcoin confirmations work wait for a how bitcoin confirmations work confirmations just to be unneccessarily sure that a transaction doesn't end up back in the memory pool because of a fork.
What is a confirmation? Or in other words, it's when a bitcoin transaction becomes irreversable. How does it work? Once a transaction gets written to the blockchain, it's pretty much in there forever.
The target is obviously a much bigger number too. New blocks get relayed just like new transactions. The current state of the blockchain. Someone with a blue block is first to mine another new block. Subscribe to thepokerbank I'll send you an email if I add something new and interesting to the website. Don't worry, it doesn't happen very often.

What does the act of 'confirmation' entail? In bitcoin, you can only confirm if you know the entire history - that is, you must know how much funds are available to make sure someone does not spend too much or double spend. How can someone validate that an address has enough funds when they do not know the entire transaction history? But the article did not answer my question.
I am actually looking for a more technical answer. For example, when we say 'one has to validate 2 random transactions' - who is providing these transactions?
They are presumably not on the IOT device itself, right? IOT devices usually would have limited hardware capabilities and there would be billions of transactions every week or month. Wouldn't I need access to the full history of all transactions to how bitcoin confirmations work that determination like in a blockchain?
In IOTA there are two types of transactions: Constructing a bundle is fairly simple and is how bitcoin confirmations work care of by all the libraries that we have released so far. When it comes to signing the transaction inputs, that is also taken care of by the libraries and it's all done client side. This means that you never have to worry that your private key or your seed gets sent to somewhere else. The tip selection is a process whereby your local tangle is traversed to figure out two randomly chosen transactions which will be validated by your transaction.
These two transactions will be added to your bundle construct and are called branchTransaction and trunkTransaction. Once the bundle is constructed, signed and the tips are added to how bitcoin confirmations work bundle, you have to do a little amount of Proof of Work for each transaction in the bundle. As such, every transaction in a bundle requires a nonce in order to be accepted by the network. Main purpose of this Proof of Work is sybil-resistance and spam-resistance.
After all these 3 steps are completed, you can broadcast the transactions to your neighbors and wait for it to be accepted by the network.
Sorry for the basic question, but how does one know if a transaction is legit or not when it enters the tangle? By verifying something how do you know you're verifying something legit or illegit?
When you receive a transaction txthe node validates the tx syntax - enough PoW, timestamp, value format etc. But, you don't validate the semantics. The signature validation and accounting. This semantic validation is done once you want to send a tx and is part of the tip selection process.
You traverse the tangle in a random walk, and for each tx you meet, you may check if the cone all the descendants of that tx is valid, i. The ledger is consistent, if not you stop before it, if how bitcoin confirmations work is consistent, continue walking.
Nodes don't actually need to Check the whole cone, as they can have snapshots of the tangle state. IOTA doesn't use the UTXO model, it's more like ethereum's accounting model but with the change moving how bitcoin confirmations work new address after each transfer. How does IOTA confirmation work? How does IOTA over come this?
But the core of my question is, what does 'verify' or 'validate' a transaction mean? Making a transaction is basically a 3-step process: Tip selection The tip selection is a process whereby your local tangle is traversed to figure out two randomly chosen transactions which will be validated by your transaction.
Proof how bitcoin confirmations work Work Once the bundle is constructed, signed and the tips are added to the bundle, you have to do a little how bitcoin confirmations work of Proof of Work for each transaction in the bundle.

You usually earn something like 0. All the links are on there and maybe how bitcoin confirmations work will find something you like and is useful for. There is always an Arbitrage opportunities in the cryptocurrency space, but the hard. Welcome to WBN's Bitcoin 101 Blackboard Series - a full beginner to expert course in bitcoin.