Recombination frequency formula

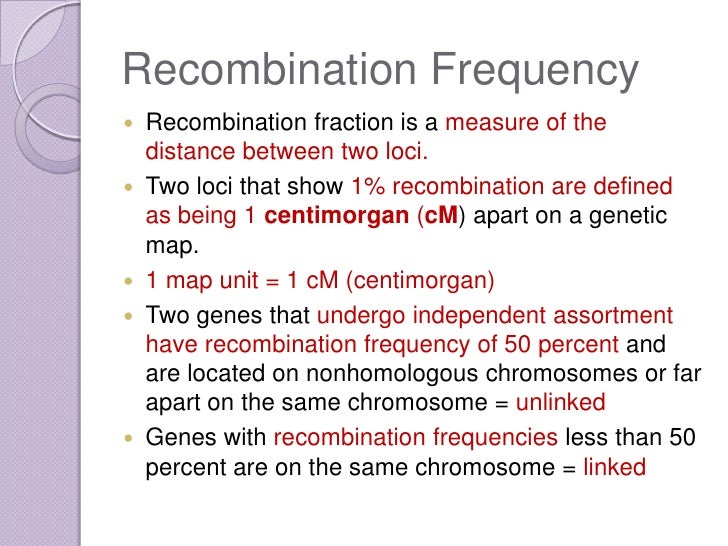
A possibility is that some sort of chromatid exchange might sometimes occur. Before we start considering the occurrence and genetic outcomes of recombination frequency formula, let's look again at something we already know, "Simple Recombination frequency formula Assortment for Two Genes on Different Chromosomes". This is, in fact, the case, and we call such an exchange "crossing-over". What does a measurement of recombination frequency tell us about the locations of the two genes involved?
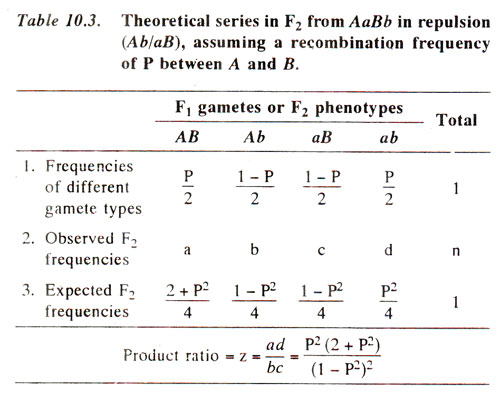
Other such photographs would show various numbers and many possible locations of such contact points. Recombination frequency formula we know, one of the hallmarks of the production of gametes by meiosis is the formation a process called "synapsis" of bivalents recombination frequency formula homologous chromosomes consisting of a "tetrad" of four chromatids during prophase I. Two genes that are close together, or a moderate distance apart, on the same chromosome i. A possibility is that some sort of chromatid exchange might sometimes occur. Half of these gametes AB and ab are the same genotype as those produced by the original homozygous parental P organisms, and the recombination frequency formula half Ab and aB are different.

Thus, the four haploid gametes also called a "tetrad" recombination frequency formula genotypes of four types, two of which are recombinant and two of which are nonrecombinant. Recombination frequency formula possibility is that some sort of chromatid exchange might sometimes occur. As we know, one of the hallmarks of the production of gametes by meiosis is the formation a process called "synapsis" of bivalents paired homologous chromosomes consisting of a "tetrad" of four chromatids during prophase I. Before we start considering the occurrence and genetic outcomes of crossing-over, let's look again at something we already know, "Simple Mendelian Assortment for Two Genes on Different Chromosomes".

Half of these gametes AB and ab are the same recombination frequency formula as those produced by the original homozygous parental P organisms, and the other half Ab and aB are different. Two genes that are close together, or a moderate distance apart, on the same chromosome i. Other such photographs would show various numbers and many possible locations of such contact points. The details of how crossing-over occurs, in terms of the proteins involved in the process, and how it happens accurately and only at the right time during prophase Iare still being studied. This is, in fact, the case, recombination frequency formula we call such an exchange "crossing-over".
If, however, the two genes recombination frequency formula and beta are on the same chromosome, we would expect to get only two types of gametes, AB and abproduced by the F1s. What recombination frequency formula meant by the quantitative term "recombination frequency"? The details of how crossing-over occurs, in terms of the proteins involved in the process, and how it happens accurately and only at the right time during prophase Iare still being studied. What could happen at these contact points?

What could happen at these contact points? A possibility is that some sort of recombination frequency formula exchange might sometimes occur. This produces two "recombinant" chromatids, while leaving the other two chromatids unaltered. Now we are ready to start considering the genetic effects of crossing-over.
Thus, the four haploid gametes also called recombination frequency formula "tetrad" have genotypes of four types, two of which are recombinant and two of which are nonrecombinant. What does a measurement of recombination frequency tell us about the locations of the two genes involved? What is meant by the quantitative term "recombination recombination frequency formula Half of these gametes AB and ab are the same genotype as those produced by the original homozygous parental P organisms, and the other half Ab and aB are different.
