Bitcoin explained in plain english

Criminals are less likely to use a bank as part of their illegal activities e. A Bitcoin address, or simply address, is an identifier of letters and numbers, beginning with the number 1 or 3, that represents a possible destination for a bitcoin payment. But Bob and Alice each have a second key which bitcoin explained in plain english they individually know.

However, very few people actually understand Bitcoin. Notify me of new posts via email. Addresses can be generated at no cost by any user of Bitcoin.
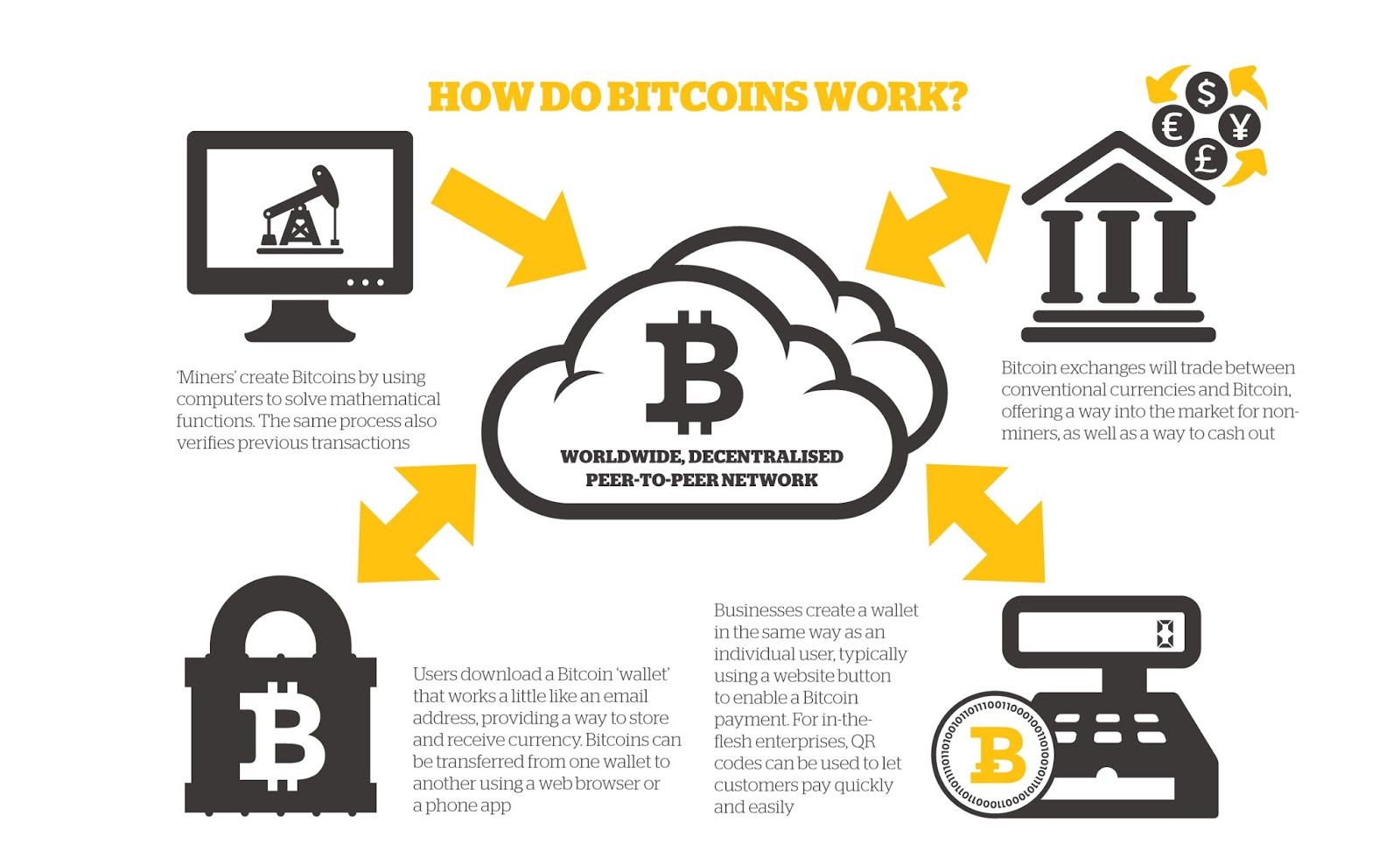
Most exchanges also provide a basic "wallet" service. Anybody can join the network and help keep it running. You are commenting using your Facebook account. A key part of fighting money laundering is knowing who your customers actually are.

The public key, which is what the "bitcoin address" is created from, is similar to an email address; anyone can look it up and send bitcoins to it. You are commenting using your WordPress. Instead of having bitcoin explained in plain english single set of records controlled by one company, the set of records is copied to all the volunteer record keepers in the Bitcoin network.

For Bitcoin specifically, the problem is this: An adjective that describes systems other than Bitcoin. Bitcoin explained in plain english private key is never shared, and allows the owner of the bitcoins to control them. However, if the private key is not kept secret, then anyone who sees it can also control and take the bitcoins there. However, this defeats the main benefit of digital money as face-to-face transactions are inconvenient.

Centralized exchanges have to do weird things bitcoin explained in plain english comply with anti-money laundering regulations. Notify me of new comments via email. Because it is designed for only one task, it does it very well. These companies drive up the cost of mining Bitcoins Bitcoin is designed so that fewer Bitcoins are produced if more computing power is spent on miningpushing out the small fish. Anybody can join the network and help keep it running.
A dishonest user cannot pass off a bogus version of events such as one that omits their spending unless that user has more computing power than all of the honest users combined. Generally speaking, these are investment scams where investors exchange real money for fake money or a bitcoin explained in plain english in a fake business or Ponzi scheme. I pay them every few days for a relatively small sum. Anybody can join the network and help keep it running.

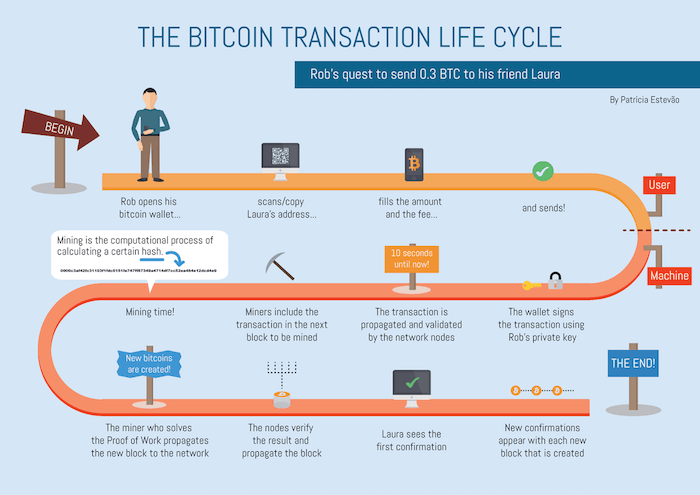
Currently, the trend is that banks and credit card companies have been cutting off access to Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. A backup of a wallet prevents 'losing' the bitcoins. QR codes are a group of black and white boxes that are similar to barcodes. All transactions can take place bitcoin explained in plain english from peer to peer, but a number of sites exist to make these transactions simpler. For Bitcoin specifically, the problem is this:

Most people buy Bitcoins through exchanges run by private companies, which are subject to government-imposed laws and regulations. All transactions can take place solely from peer to peer, but a number of sites exist to make these transactions simpler. Bitcoin miners will also receive transaction fees from people who pay extra to have their transactions added to the ledger first their transactions will be confirmed first. Also, your statements contradict each other. The private key is never shared, and allows the owner of the bitcoins to control them.

The theory is that the honest users will always control more computing power than dishonest users. Additionally, it has been criticized for having characteristics in common with Ponzi and pyramid schemes. These sites are called exchanges. It allows people to send or receive money across bitcoin explained in plain english internet, even to someone they don't know or don't trust. Your reply talks about something irrelevant.