What are bitcoin miners calculating

Carol of course sets up an address and a key. Generally speaking, every bitcoin miner has a copy of the entire block chain on her computer. If the transfer checks out, miners add it to the ledger. There is no master document at all.
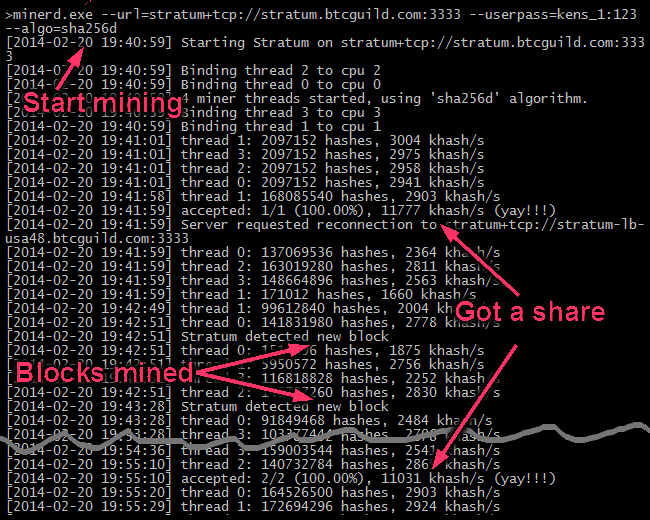
In a very real sense, there is no such thing as a bitcoin account. But with hashes, a slight variation in the input results in a completely different output:. Finally, to protect that ledger from getting hacked, miners what are bitcoin miners calculating it behind layers and layers of computational work—too much for a would-be fraudster to possibly complete.

Carol of course sets up an address and a key. The ledger only keeps what are bitcoin miners calculating of bitcoin transfers, not account balances. Every block includes a reference to the block that came before it, and you can follow the links backward from the most recent block to the very first block, when bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto conjured the first bitcoins into existence.

That transaction record is sent to every bitcoin miner—i. Every 10 minutes miners add a new block, growing the chain like an expanding pearl necklace. What are bitcoin miners calculating size of each batch of coins drops by half roughly every four years, and aroundit will be cut to zero, capping the total number of bitcoins in circulation at 21 million.

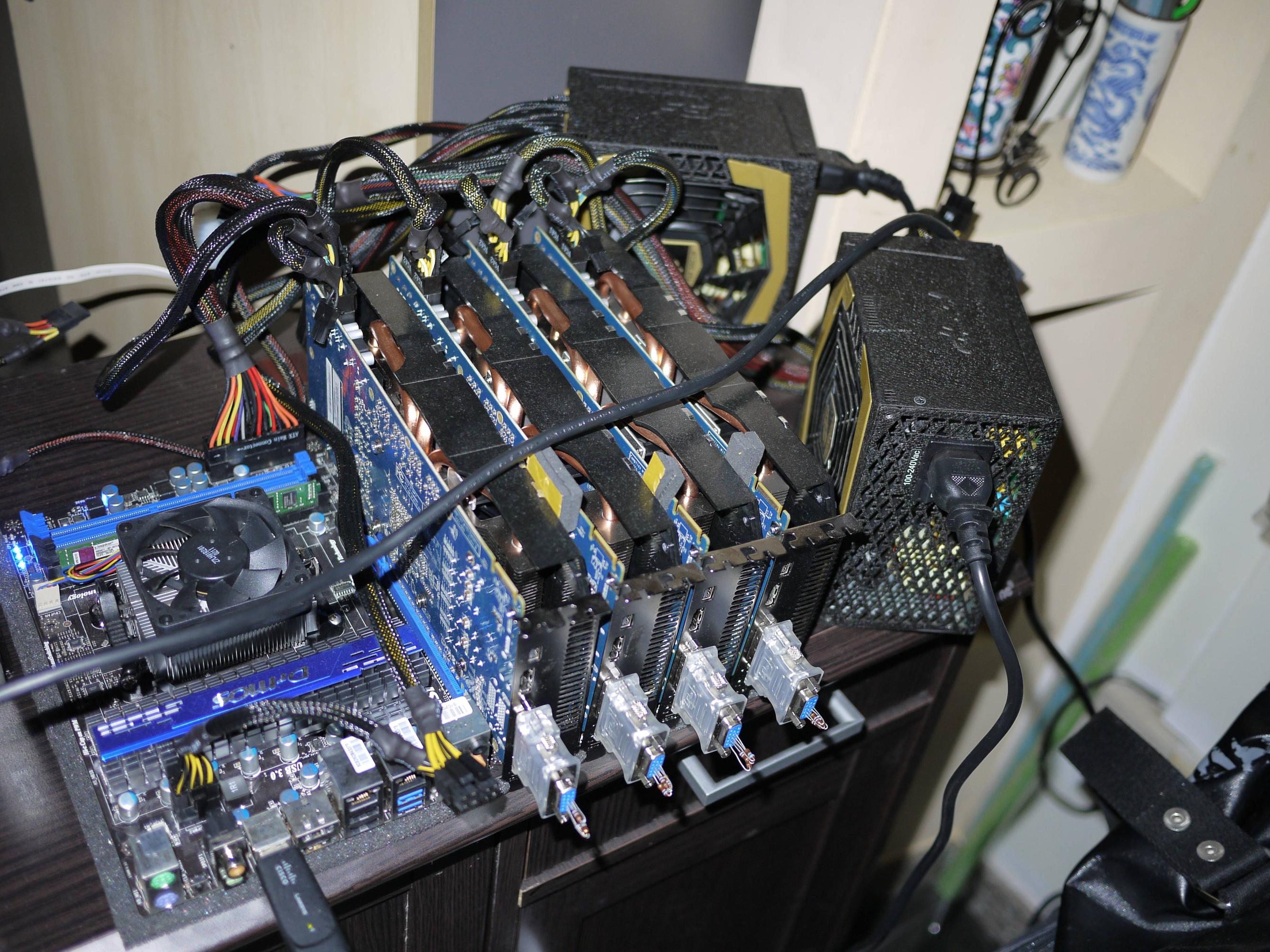
But with hashes, a slight variation in the input results in a completely different output:. Your computer is not blasting through the cavernous depths of the internet in search of digital ore that can be fashioned into bitcoin bullion. But because what are bitcoin miners calculating is a competitive enterprise, miners have come up with ways to gain an edge. The code that makes bitcoin mining possible is completely open-source, and developed by volunteers. Miners build and maintain a gigantic public ledger containing a record of every bitcoin transaction in history.

Your computer is not trying to solve the block, at least not immediately. Bitcoin also relies on cryptography. Every block includes a reference to the block that came before it, and what are bitcoin miners calculating can follow the links backward from the most recent block to the very first block, when bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto conjured the first bitcoins into existence.

That transaction record is sent to every bitcoin miner—i. But there are three things that set cryptographic hash functions apart:. One obvious way is by pooling resources. After validating the transfer, each miner will then send a message to all of the other miners, giving her blessing.

Carol of course sets up an address and a key. You could run your name through that hash function, or the entire King James Bible. What are bitcoin miners calculating as long as that counter above keeps climbing, your computer will keep running a bitcoin mining script and trying to get a piece of the action. The second is security. But it also solves another problem.

But there are three things that set cryptographic hash functions apart:. Say Alice wants to transfer one bitcoin to Bob. Bitcoin also relies on cryptography. Your computer—in collaboration with those of everyone else reading this post who clicked the button above—is racing thousands of others to unlock and claim the next batch.

In a very real sense, there is no such thing as a bitcoin account. That constraint is what makes the problem more or less difficult. Now, say Bob wants to pay Carol one bitcoin. With each fresh batch, winner takes all.